| description |
cgs |
unit |
SI (mks) |
unit |
factor |
| acceleration |
galileo |
Gal |
metre per second squared |
m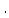 s s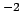 |
0.01 |
|
dynamic viscosity |
poise |
P |
pascal second |
Pa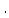 s s |
0.1 |
|
electric charge |
franklin |
Fr |
coulomb |
C |
3.34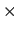 10 10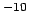 |
|
electric current |
biot |
Bi |
ampere |
A |
10 |
|
electric dipole moment |
debye |
D |
coulomb metre |
C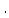 m m |
3.34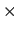 10 10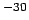 |
|
energy (work) |
erg |
|
joule |
J |
10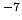 |
|
force |
dyne |
dyn |
newton |
N |
10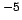 |
|
heat energy |
calorie |
cal |
joule |
J |
4.187 |
|
heat transmission |
langley |
|
kilojoule per square metre |
kJ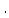 m m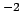 |
41.84 |
|
illumination |
phot |
ph |
lux |
lx |
10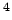 |
|
kinematic viscosity |
stokes |
St |
square metres per second |
m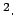 s s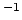 |
10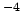 |
|
|
lambert |
Lb |
|
|
3183.1 |
|
|
stilb |
sb |
|
magnetic dipole moment |
emu |
|
ampere square metre |
A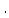 m m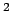 |
10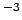 |
|
magnetic field strength |
oersted |
Oe |
ampere per metre |
A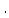 m m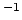 |
79.577 |
|
|
line |
li |
|
|
10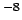 |
|
|
maxwell |
Mx |
|
|
unit pole |
|
|
magnetic flux density |
gauss |
G |
tesla |
T |
10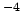 |
|
magnetomotive force |
gilbert |
Gi |
ampere |
A |
0.796 |
|
permeability |
darcy |
|
square metre |
m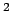 |
0.987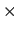 10 10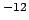 |
|
pressure |
barye |
ba |
pascal |
Pa |
0.1 |
|
wave number |
kayser |
K |
per metre |
m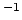 |
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|