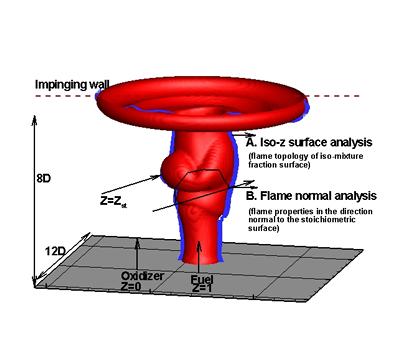
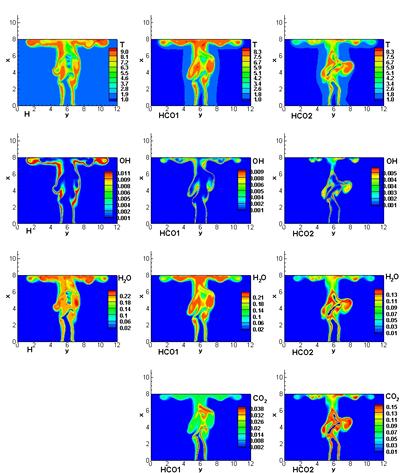
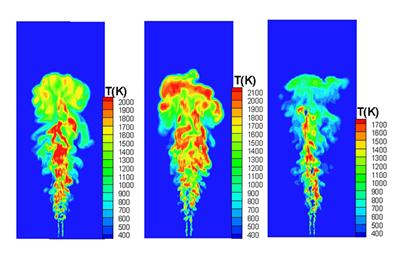
Research project: High-Hydrogen Content Alternative Fuel Burning
A tremendously important new climate change mitigation technology is clean combustion, which can significantly reduce carbon dioxide emission while continuing to use fossil fuels, such as coal, shale gas, for power generation. In moving towards high efficiency power generation systems with reduced emissions, the use of high-hydrogen content fuels becomes increasingly attractive. Therefore, developing a basic understanding of high-hydrogen content fuel burning has relevance to many situations such as cleaner electric power generation with reduced carbon dioxide emissions.