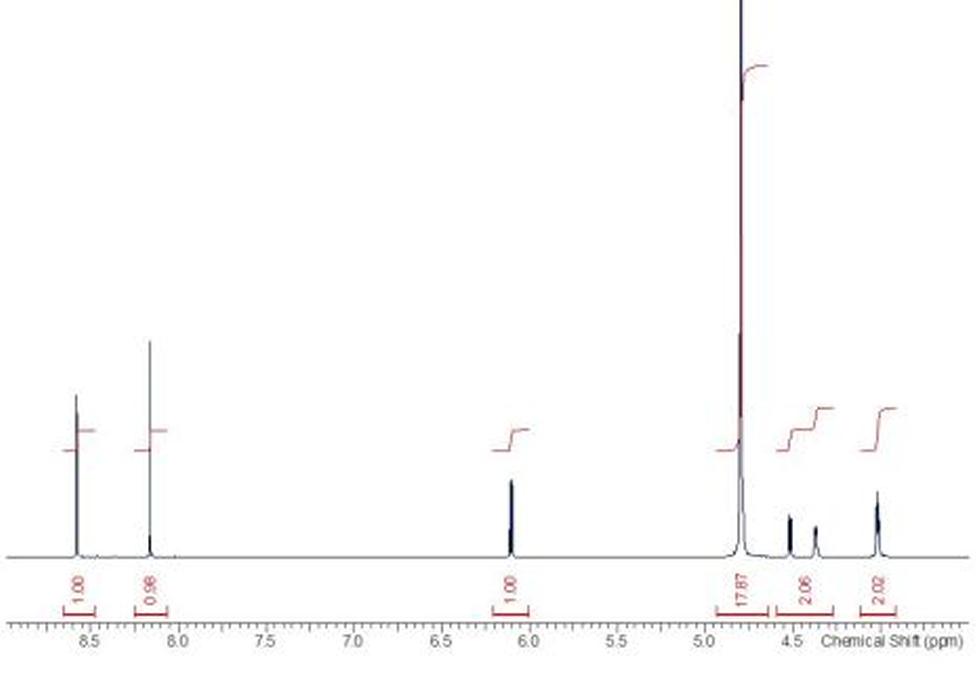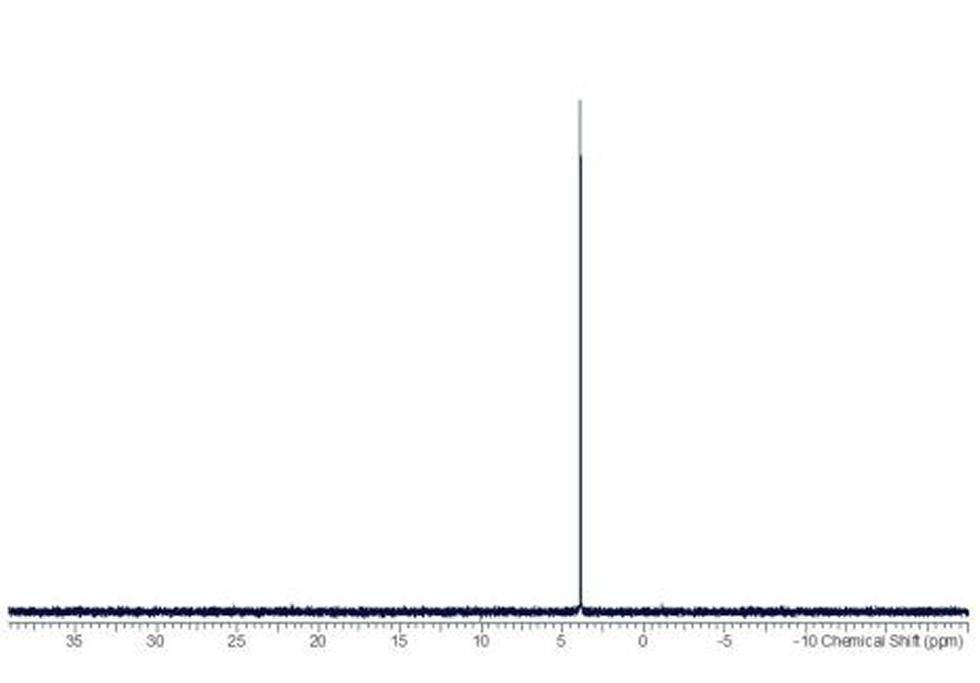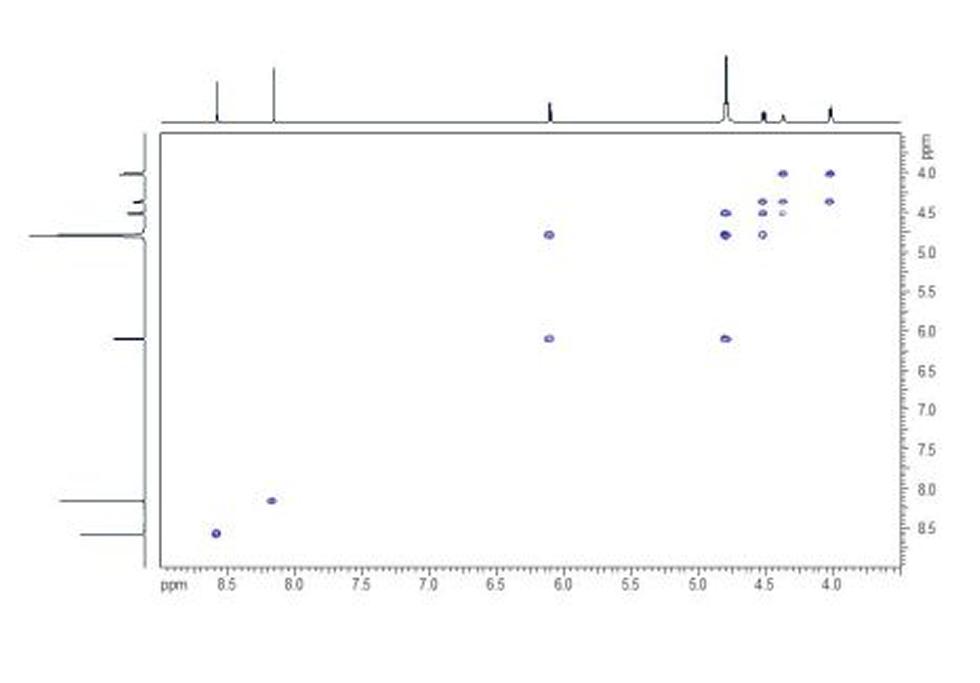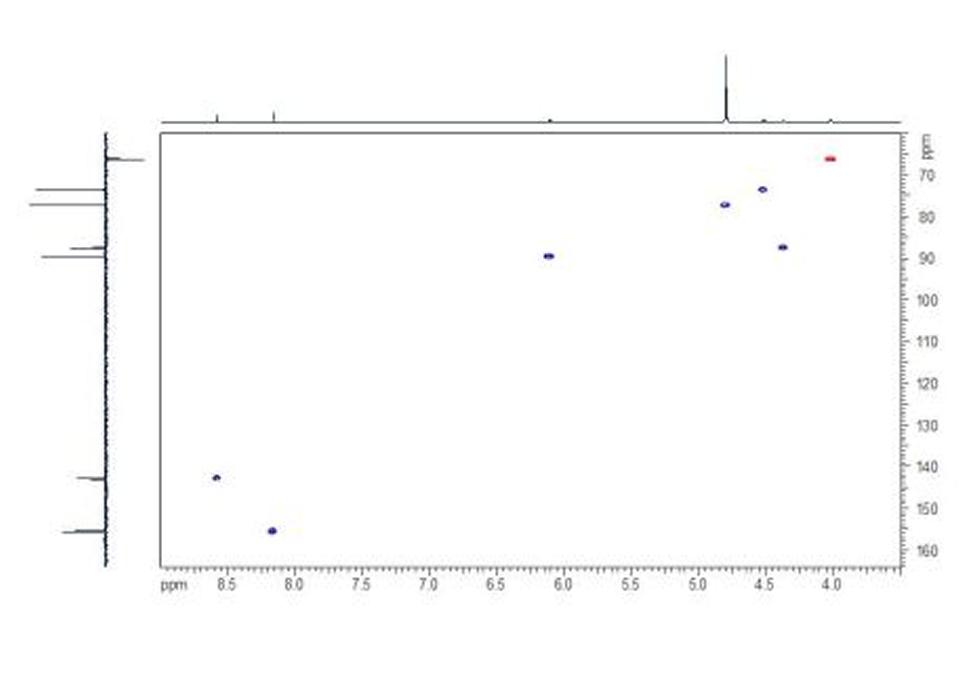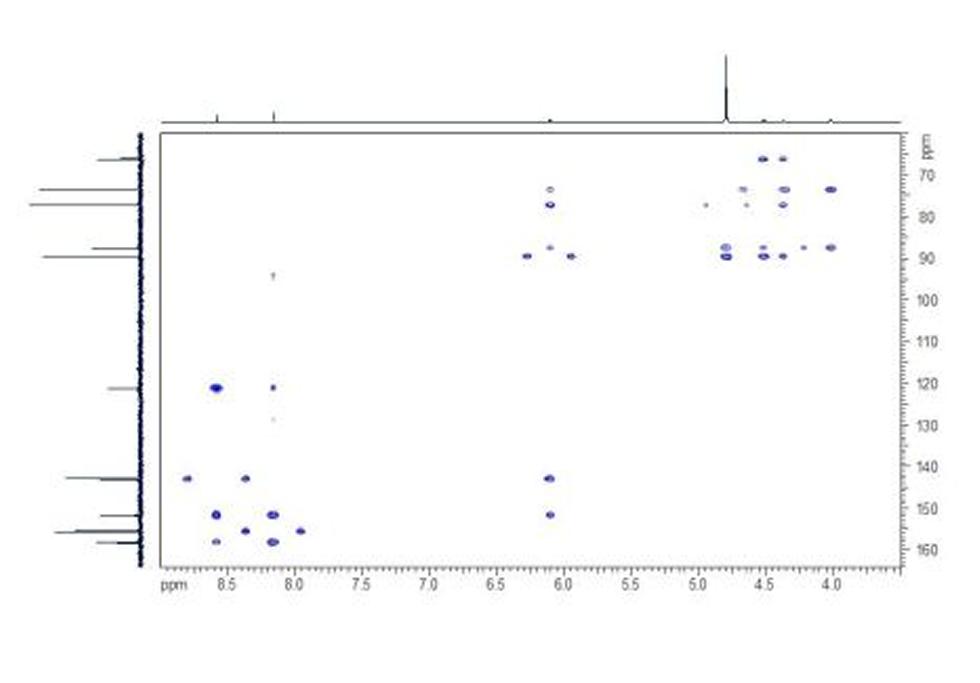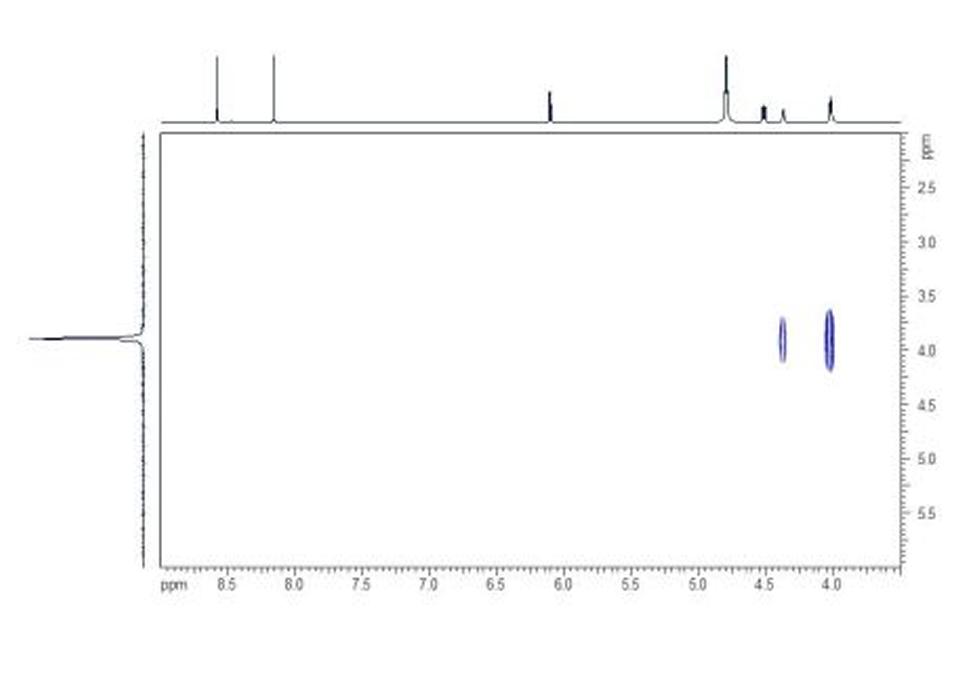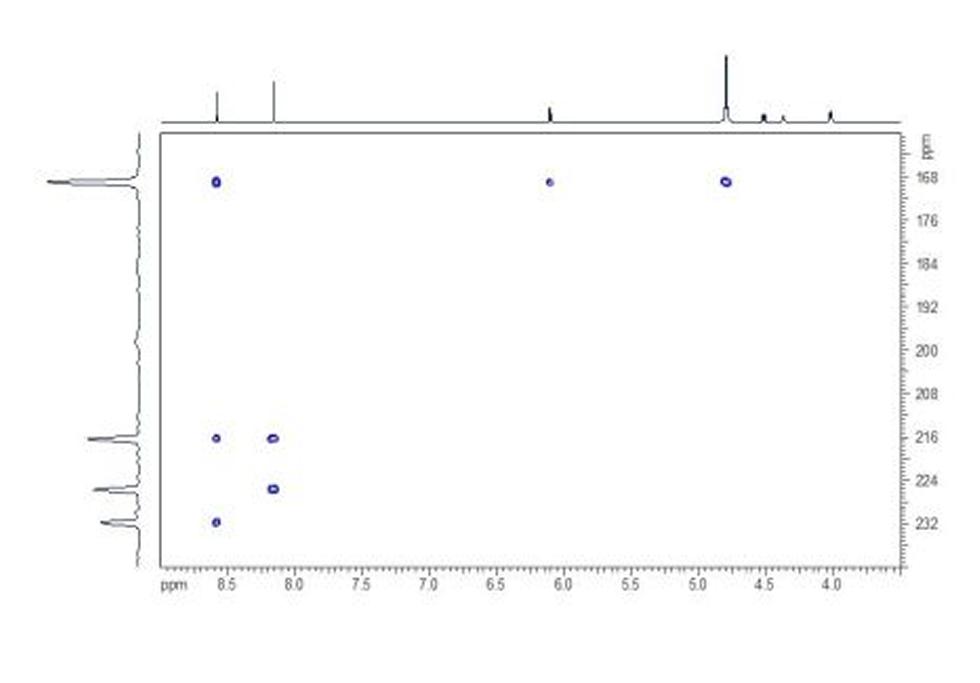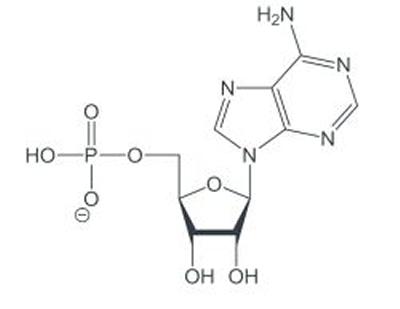
Adenosine monophosphate (AMP), also known as 5'-adenylic acid, is a nucleotide that is used as a monomer in DNA and RNA. It is an ester of phosphoric acid and the nucleoside adenosine. AMP consists of a phosphate group, the sugar ribose, and the nucleobase adenine.
Data Collection
Bruker AVIIIHD500 FT-NMR spectrometer
5 mm SMART probe