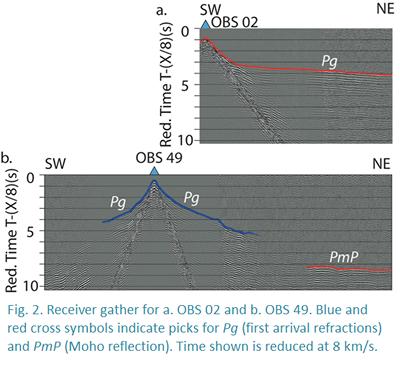
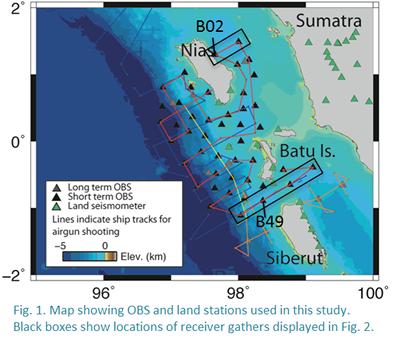
Research project: Active-source seismic refraction across the Sumatra subduction zone
Historic earthquakes have ruptured distinct segments of the plate boundary megathrust at the Sumatra subduction zone. We use seismic refraction data to derive a velocity model for a 3-D area crossing the plate boundary near Nias and Siberut (Fig. 1). Seismic refraction datasets can shed light on factors controlling rupture segmentation [e.g., Tang et al., 2013].