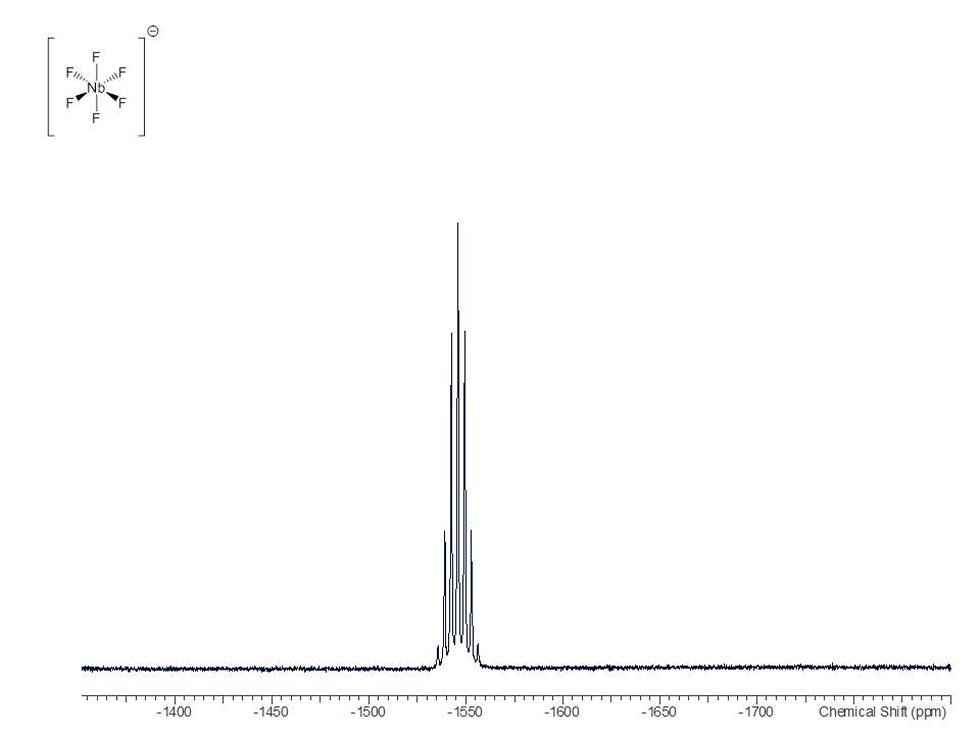
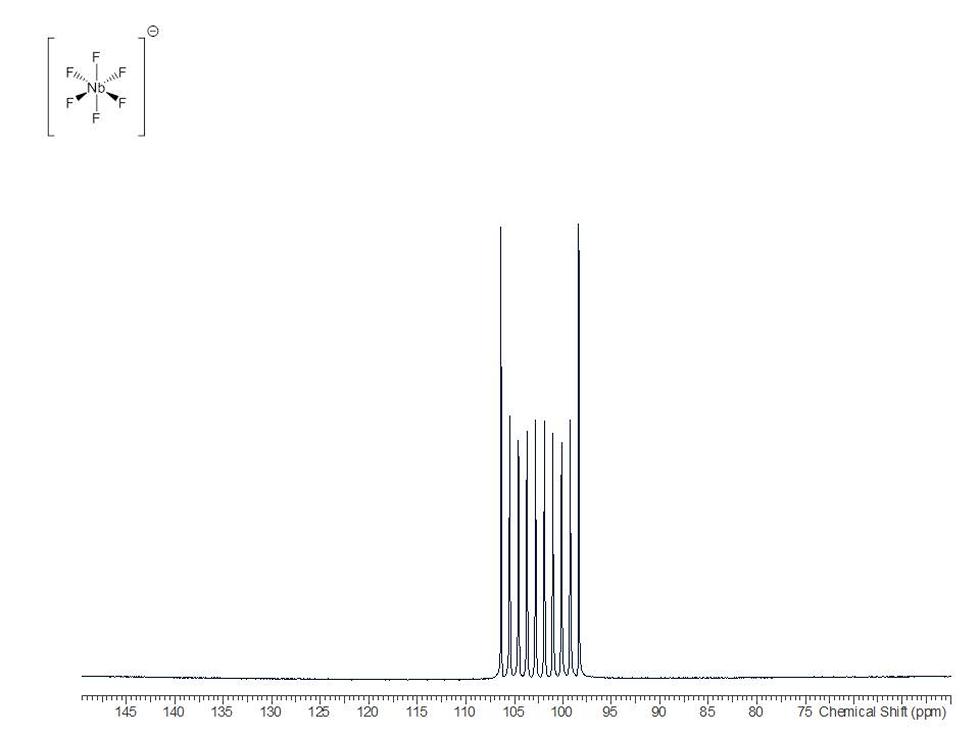
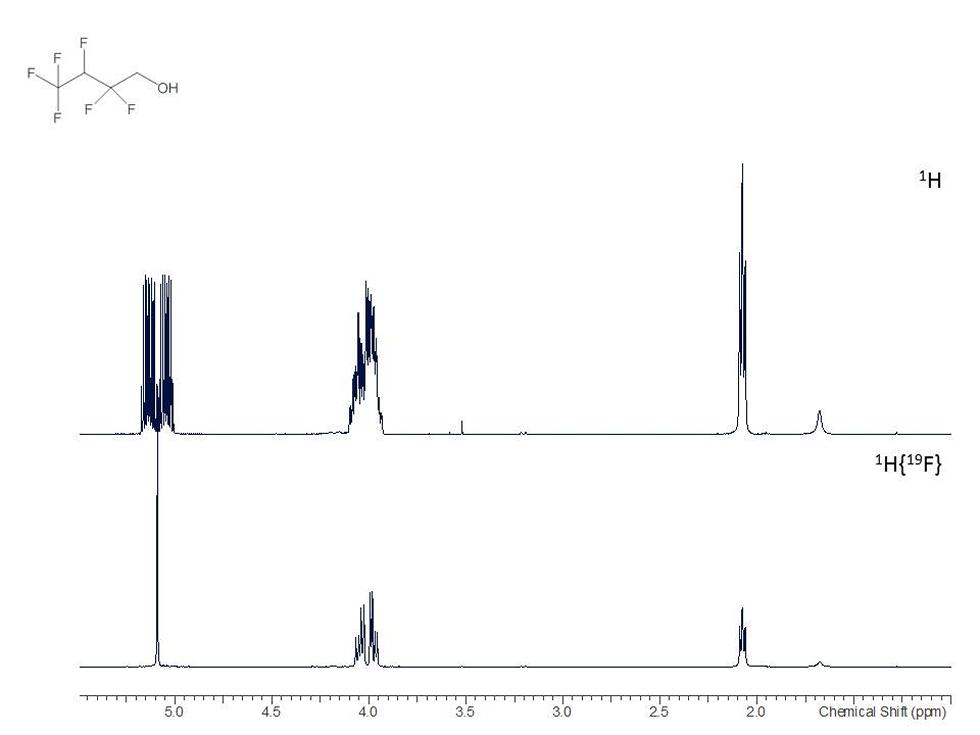
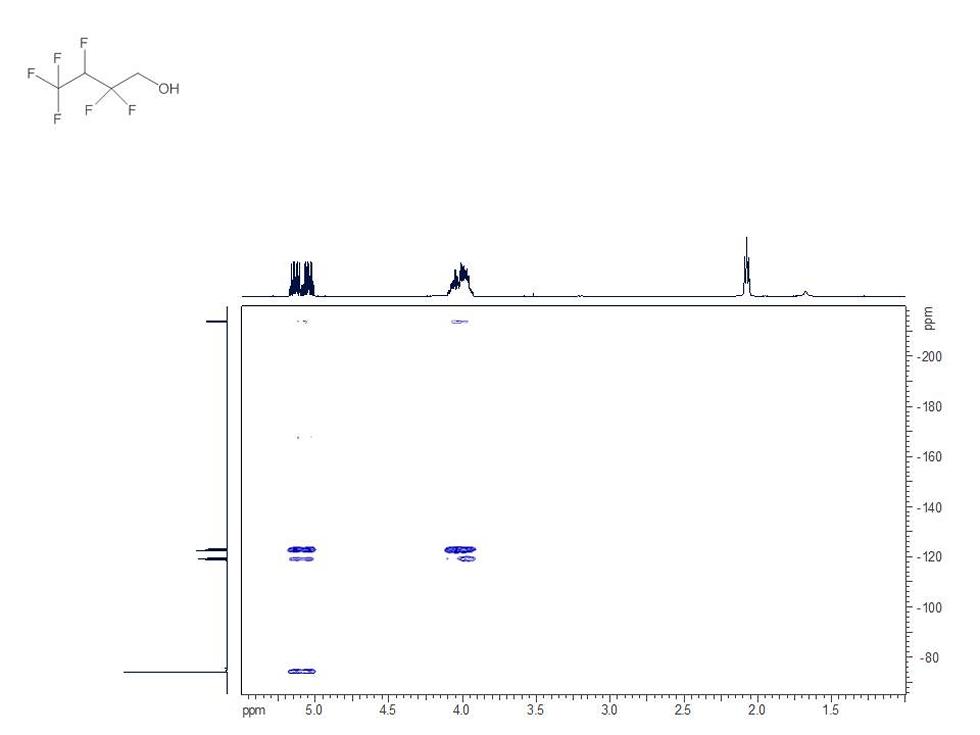
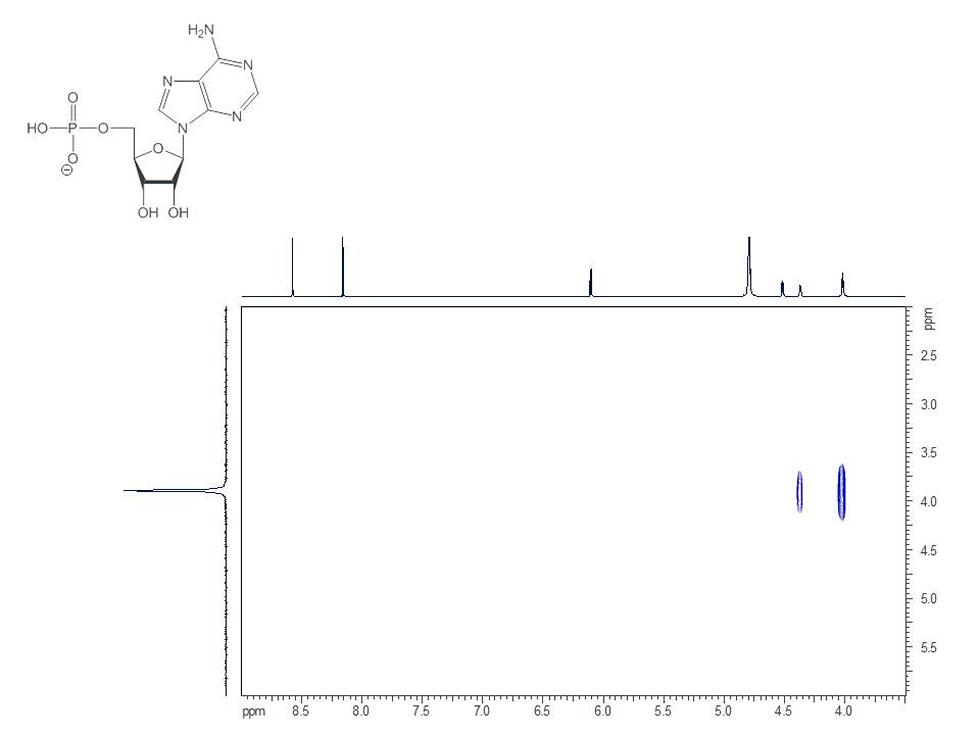
Many compounds can be better studied using nuclei other than 1H and 13C:
Use of multinuclear NMR spectroscopy enables such parameters as oxidation state, complexation geometry and fluxionality of organometallic complexes and inorganic salts to be probed.
19F is a very sensitive NMR active nucleus that provides a wealth of structural detail. The chemical shift information and coupling data (between fluorine nuclei and other atoms) found in 19F NMR spectra allows the assignment of both the nature and location of fluorine atoms within molecules.