- Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) is an illness which may occure during the birth in new borns due to the shortages of oxygen reaching to their brains. The shortages of oxygen may damage some part of the brain which may lead to some abnormalities in their behaviour once they are grown up.
- The first objective of this project is to find out if new born babies are suffering from HIE by analysing their MR images (SWI) by using Computer Vision and Image Analysis techniques.
- The second objective here is to find out what part of their brains have been damaged due to HIE to predict what behavarial abnormalities will be observed, once they are grown up.
- To achieve these two objectives, initially MR images are processed and cleaned from noise and artifacts. Then various features are extracted from MR images by using computer vision techniques. Such features are finally fed to a classifier for the diagnosis of illness.
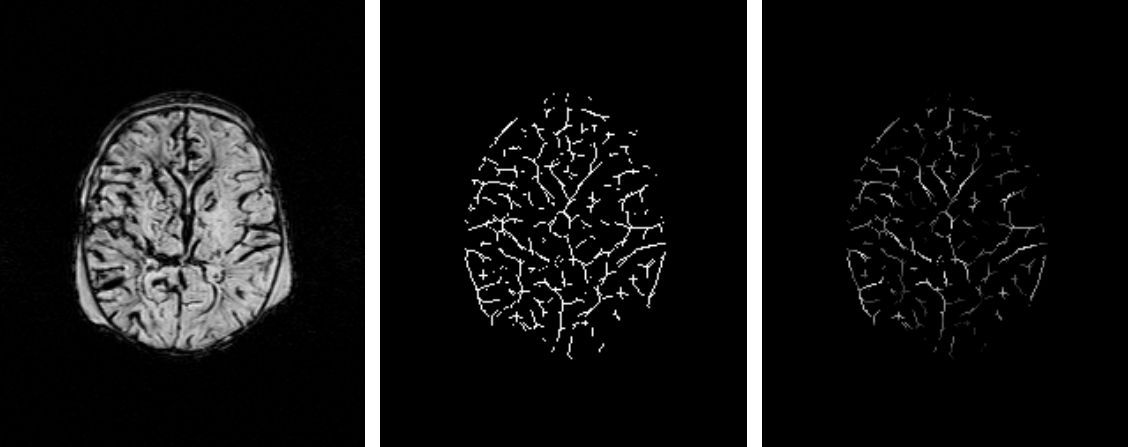
- In the above figure, the image in left shows a SW image taken from a new born baby with HIE, the vessels are detected as shown in the image in the middle and finally the detected vessels are given a weight (brightness) corresponding to how much the vessel is affected by HIE [1].
- By using features such as those (weights) shown in the right image of the above figure, we can determine if a new born baby's brain has been damaged by HIE and then predict the patient's behaviour outcome in the next two or three years [1,2].
[1]- Wu, Sisi, Mahmoodi, Sasan, Darker, Angela, Vollmer, Brigitte, Lewis, Emma and Liljeroth, Maria (2017) Feature extraction and classification to diagnose hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy patients by using susceptibility-weighted MRI images. In Medical Image Understanding and Analysis. MIUA 2017. vol. 723, Springer. 11 pp . (doi:10.1007/978-3-319-60964-5_46).
[2]- Citraro, Leonardo, Mahmoodi, Sasan, Darker, Angela and Vollmer, Brigitte (2017) Extended three-dimensional rotation invariant local binary patterns. Image and Vision Computing. Vol. 62, pp. 8-18. (doi:10.1016/j.imavis.2017.03.004).

