Infectious prions are misfolded, β-sheet isoforms of the host encoded cellular prion (PrPc) protein that are the causative agents in transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSE) including bovine spongiform encephalopathy and Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease.
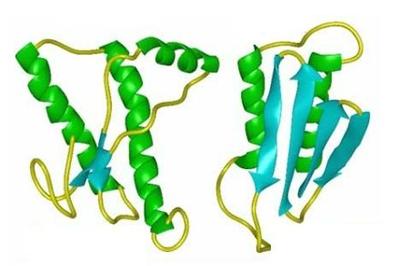
Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathies (TSE’s) or prion diseases are a group of rare, transmissible, and fatal, brain diseases, of which probably the most well-known are Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE) in cattle and Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD) in humans. This group of disorders have been coined prion diseases due to the widely held belief that the main protagonist of the disease is a naturally occurring, but mis-folded, protein; and it is this proteinaceous infectious particle that has provided the basis for the term prion.
CJD itself can be split into three distinct sub-types:
- Familial CJD. An inherited form of CJD in which offspring inherited a mutation within their genome causing the onset of CJD in later life.
- Sporadic CJD. Currently the most prolific of the human TSE’s with recorded incidences of around 0.5 – 1 person per million. Sporadic CJD is considered to occur when there is either random mutation in the prion protein or its gene.
- Acquired CJD. A form of CJD that is by definition, obtained through a third party source. An example being variant CJD which is linked to the consumption of infected beef products, or iatrogenic CJD, where infection is induced inadvertently by the medical treatment or procedures or activity of a physician.
At the University of Southampton work on the elimination of iatrogenic CJD has been initiated.